What is Circuit Switching?
This method of switching establishes a dedicated communication path between the sender and receiver. Here the link is established in physical form between two stations present in the network. The link will be established, maintained and terminated for each communication session. The most common example of circuit switching is the Analog telephone network.
This method of switching provides a constant bit delay and fixed data rate channel between the sender and receiver. The full channel capacity is dedicated for the duration of a connection. When data is to be transferred from sender to receiver, firstly the sender sends a request to the switching station for the establishment of a connection. The receiver replies with an acknowledgment. After receiving the acknowledgment signal the sender starts the data transmission. This switching is commonly used for voice circuits. The public switched telephone network, Datakit, B channel of ISDN, Optical mesh network, etc are some of the examples of circuit-switched networks.
Circuit Switching Diagram
In this type of switching, there is a set of switches connected with physical links. Here once the dedicated path is established between the sender and receiver, it stays the same until one of the users terminates the connection. Fixed data is transmitted and this type of switching is highly used to transfer voice data. The network consists of the switching offices with permanent links between them. Whenever is connection requested the communication links are dedicated to the terminals forming the transmission route. This dedicated link is maintained until the connection is terminated. Other users will be able to use this link only when it is terminated by the sender or receiver.
There are three phases in the establishment of a circuit switching network. They are – circuit establishment, Data transfer and circuit disconnect.

Circuit Establishment
This is the circuit setup phase. Here the link is established between the sender and receiver. When a connection has to be established between station A and station B, station A sends a connection request to node 1 through a dedicated link between station A and node1. Then node1 sends the request to all the nodes connected to it. The request is forwarded among the nodes finally forming a route to the Station B. Based on its status station B sends the acknowledgment if it is not busy. Thus a dedicated communication link will be established between Station A and Station B.
Differences Between Circuit Switching and Packet Switching
- In-circuit switching, data is transmitted continuously between the sender and receiver. Whereas in packet switching the data is packetized and sent independently over a shared network.
- When the connection is maintained in the circuit switching no other user can access that link, even when no data is been transmitted. Thus circuit switching provides high-quality service.
- In packet switching the bandwidth is shared by the users. Thus, the quality of the service is low in packet switching.
- Unlike circuit switching, the path is not reserved in the packet switching network. Packet switching supports store and forward transmission.
- No physical path is established for the packet switching network.
- Packet switching is more efficient compared to circuit switching.
- Packet switching infrastructure is less complicated compared to circuit switching.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Some of the advantages of circuit switching are as follows –
- It uses a fixed bandwidth.
- A dedicated communication channel increases the quality of communication.
- Data is transmitted with a fixed data rate.
- No waiting time at switches.
- Suitable for long continuous communication.
Some of the disadvantages of circuit switching are as follows-
- A dedicated connection makes it impossible to transmit other data even if the channel is free.
- Resources are not utilized fully.
- The time required to establish the physical link between the two stations is too long.
- As a dedicated path has to be established for each connection, circuit switching is more expensive.
- Even if there is no transfer of data, the link is still maintained until it is terminated by users. By this channel remains ideal for a long time thereby making circuit switching inefficient.
- Dedicated channels require more bandwidth
What is Packet Switching?
Definition: Packet switching refers to a set of protocols that uses a connection-less network switching approach to transmit the packets. In this switching, the messages are broken and grouped into small units called packets. These packets are transmitted individually across a digital network to reach its destination. Packets need not follow the same route to reach their destination. As all the packets arrive at a destination in a different order, the original message is recompiled by the destination itself. The packet switching diagram is shown below.
In this switching, packets have two parts – a header and a payload. The information in the header allows networking hardware/intermediate node to make sure that the packets are directed towards its destination, while the definite data is carried by the payload.
Each packet has a source and destination address to travel independently over a network with a variable bitrate. Packets are forwarded asynchronously by intermediate nodes because of congestion, queuing, and so on, and hence follows different routes. These packets arrive at the destination in a different order, and the destination ensures to reassemble the data of the same file.
The message consists of four packets – A, B, C, and D. Each packet consists of source and destination address and follows more than one route to reach the destination from source as shown in the figure below.

Advantages of Packet Switching Over Circuit Switching
This switching offers various benefits compared to circuit switching and they are listed below:
- It delivers the data to a destination by finding their own paths; circuit switching has a dedicated and predefined channel.
- It is highly reliable as missing packets are detected by destination; circuit switching does not have this option.
- It uses lesser bandwidth as packets are quickly routed towards the destination; circuit switching should have dedicated bandwidth.
- The channel in this switching is available for other transmissions as soon as packets are routed; circuit switching occupies the channel till the voice communication is completed
- It is cost-effective and easier to implement; circuit switching is expensive
Disadvantages of Packet Switching Over Circuit Switching
Despite offering various benefits, this switching offers disadvantages too, which are listed below:
- As the movement of packets is not synchronous in this switching, it may not be suitable in communication applications like voice calls; while circuit switching is highly suitable for voice calls
- Packets don’t move in an organized way, sequence numbers should be provided to identify each packet; circuit switching gives the highest priority for the channel to give the best experience to the users
- In this switching, complexity is high at each node as packets are routed over multiple paths to reach the destination, leading to loss of data or delay in delivering the packets; circuit switching makes sure there is no loss of data
- This switching needs additional and secure protocols to protect the data, leading to a significant rise in implementation costs; circuit switching has a dedicated channel for one service and one individual route.
Message switching techniques
Switched communication networks are those in which data transferred from source to destination is routed between various intermediate nodes. Switching is the technique by which nodes control or switch data to transmit it between specific points on a network. There are 3 common switching techniques:
- Circuit Switching
- Packet Switching
- Message Switching
Message Switching –
Message switching was a technique developed as an alternate to circuit switching, before packet switching was introduced. In message switching, end users communicate by sending and receiving messages that included the entire data to be shared. Messages are the smallest individual unit.
Also, the sender and receiver are not directly connected. There are a number of intermediate nodes transfer data and ensure that the message reaches its destination. Message switched data networks are hence called hop-by-hop systems.
They provide 2 distinct and important characteristics:
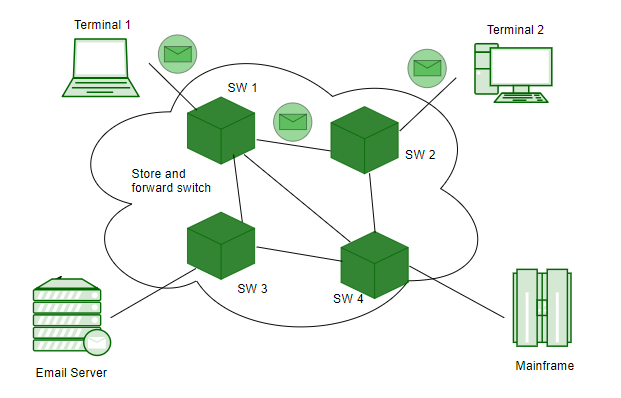
- Store and forward – The intermediate nodes have the responsibility of transferring the entire message to the next node. Hence, each node must have storage capacity. A message will only be delivered if the next hop and the link connecting it are both available, otherwise it’ll be stored indefinitely. A store-and-forward switch forwards a message only if sufficient resources are available and the next hop is accepting data. This is called the store-and-forward property.
- Message delivery – This implies wrapping the entire information in a single message and transferring it from the source to the destination node. Each message must have a header that contains the message routing information, including the source and destination.
Message switching network consists of transmission links (channels), store-and-forward switch nodes and end stations as shown in the following picture:
Characteristics of message switching –
Message switching is advantageous as it enables efficient usage of network resources. Also, because of the store-and-forward capability of intermediary nodes, traffic can be efficiently regulated and controlled. Message delivery as one unit, rather than in pieces, is another benefit.
However, message switching has certain disadvantages as well. Since messages are stored indefinitely at each intermediate node, switches require large storage capacity. Also, these are pretty slow. This is because at each node, first there us wait till the entire message is received, then it must be stored and transmitted after processing the next node and links to it depending on availability and channel traffic. Hence, message switching cannot be used for real time or interactive applications like video conference.
Advantages of Message Switching –
Message switching has the following advantages:
- As message switching is able to store the message for which communication channel is not available, it helps in reducing the traffic congestion in network.
- In message switching, the data channels are shared by the network devices.
- It makes the traffic management efficient by assigning priorities to the messages.
Disadvantages of Message Switching –
Message switching has the following disadvantages:
- Message switching cannot be used for real time applications as storing of messages causes delay.
- In message switching, message has to be stored for which every intermediate devices in the network requires a large storing capacity.
Applications –
The store-and-forward method was implemented in telegraph message switching centres. Today, although many major networks and systems are packet-switched or circuit switched networks, their delivery processes can be based on message switching. For example, in most electronic mail systems the delivery process is based on message switching, while the network is in fact either circuit-switched or packet-switched.

0 comments:
Post a Comment